Install python on wsl2 and ubuntu 22
I need to run a Python program on a Windows machine to generate an OAuth token:
https://developers.google.com/drive/api/quickstart/python
Install WSL2 - Ubuntu 22
Lets prefer to use Ubuntu on the windows machine for maximum safety of library compatibility (and it is what I know best)
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install
# from cmd.exe as administrator
wsl --install
# check which version of WSL ie 1 or 2
# and what linux distribution(s) are installed
wsl -l -v
# list of available distributions
wsl --list --online
# install 22.04. I had to do this as had an older version running in WSL
wsl --install -d Ubuntu-22.04
Then install the Terminal:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/terminal/install which is a MS Store application
# set default terminal to Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS (orange circle). Ignore the other one if there
# default text size to 10 or 9
sudo apt get update
sudo apt get upgrade
https://superuser.com/questions/1737942/different-profiles-of-the-same-wsl2-linux-instance-in-windows-terminal 2 versions discussion
Install Python and PIP and Google Client Library
What comes with 22 already?
# 3.8.10 (on Ubuntu 20) and 3.10.6 on Ubuntu 22
python3 -V
# 20.0.2 - this is old
sudo apt install python3-pip -y
# update pip to 23.0.1
pip install --upgrade pip
Why not using a virtual environment? Well, for simplicity lets install python packages on the base OS ie Ubuntu for now. I normally run inside pipenv
pip install --upgrade google-api-python-client google-auth-httplib2 google-auth-oauthlib
# if you get a dependency error in pip install above, try this, then rerun pip install
sudo apt install python3-testresources
Running the program
This is my slightly modified version of the code from https://developers.google.com/drive/api/quickstart/python as it gives a wider scope to allowed read/write access to the drive.
from __future__ import print_function
import os.path
from google.auth.transport.requests import Request
from google.oauth2.credentials import Credentials
from google_auth_oauthlib.flow import InstalledAppFlow
from googleapiclient.discovery import build
from googleapiclient.errors import HttpError
# from googleapiclient.http import MediaFileUpload
# If creating for first time download the json `credentials.json` from https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials OAuth 2.0 Client IDs
# https://davemateer.com/2022/04/28/google-drive-with-python for more information
# Can run this code to verify the token is the correct user
# and it will refresh the token accordingly
# Code below from https://developers.google.com/drive/api/quickstart/python
# If modifying these scopes, delete the file in secrets/token xxx.json.
SCOPES = ['https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive']
def main():
token_file = 'secrets/token-generated.json'
creds = None
# The file token.json stores the user's access and refresh tokens, and is
# created automatically when the authorization flow completes for the first
# time.
if os.path.exists(token_file):
creds = Credentials.from_authorized_user_file(token_file, SCOPES)
# If there are no (valid) credentials available, let the user log in.
if not creds or not creds.valid:
if creds and creds.expired and creds.refresh_token:
print('Requesting new token')
creds.refresh(Request())
else:
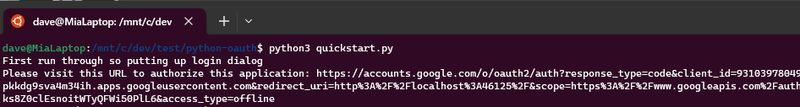
print('First run through so putting up login dialog')
# credentials.json downloaded from https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/credentials
flow = InstalledAppFlow.from_client_secrets_file('credentials.json', SCOPES)
creds = flow.run_local_server(port=0)
# Save the credentials for the next run
with open(token_file, 'w') as token:
print('Saving new token')
token.write(creds.to_json())
else:
print('Token valid')
try:
service = build('drive', 'v3', credentials=creds)
# print info about the user to prove the token works
results = service.about().get(fields="*").execute()
emailAddress = results['user']['emailAddress']
print(emailAddress)
except HttpError as error:
print(f'An error occurred: {error}')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Remember to create secrets directory, and have the credentials.json in the root
If all the dependencies are installed correctly you should see this on first run of the program.
The next step is to click on the link in the terminal, then run through the OAuth flow to get the secrets\token-generated.json
You can run this code multiple times to prove the secrets\token-generated.json token works without having to reauthenticate.